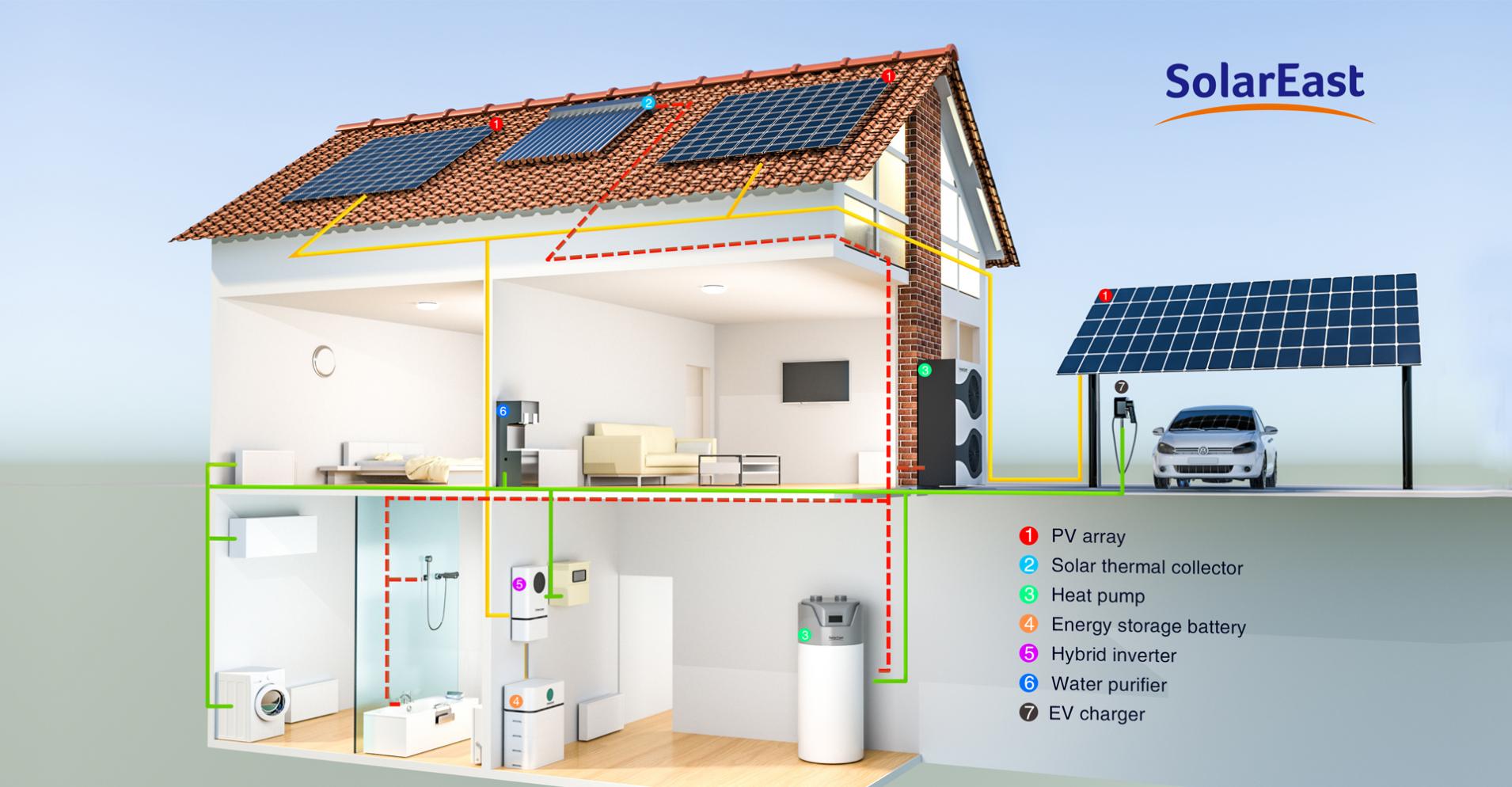
The rapid growth of electric vehicles (EVs) is a key driver of the global transition to sustainable energy. However, as EV adoption surges, the power grid faces significant pressure to meet the increased demand for electricity. Traditional grid infrastructures are often not equipped to handle the surge in energy consumption from EV charging stations. This is where Energy Storage Systems (ESS) come into play, offering an innovative solution to expand the power grid and ensure reliable, uninterrupted charging services.
The Growing Demand for EV Charging and Its Impact on the Power Grid
As electric vehicles become more popular, the power grid must adapt to meet new energy demands. The clustering of EVs in urban areas, combined with peak charging times (often during the evening), creates significant challenges for grid operators. These challenges include grid instability and the risk of overload, particularly in regions with outdated or limited grid infrastructure.
In 2022, for example, the Netherlands experienced grid instability driven by a sharp rise in EV sales. This highlighted the urgent need for smarter, more resilient energy solutions to handle the demand spikes caused by widespread EV adoption.
Countries with aging grid systems—such as Germany, the Netherlands, and parts of Eastern Europe—are especially vulnerable. The limitations of traditional grid infrastructure, coupled with long upgrade cycles and complex regulatory processes, make it difficult to expand grid capacity quickly enough to accommodate growing EV charging networks.
How ESS Can Improve EV Charging Networks
Energy Storage Systems (ESS) offer an effective and efficient solution for expanding and stabilizing the power grid. By integrating ESS with EV charging stations, operators can enhance grid stability, reduce the need for costly grid upgrades, and ensure that charging networks remain reliable, even during high-demand periods.
1. Minimizing the Need for Grid Upgrades
One of the primary benefits of ESS is its ability to reduce reliance on expensive grid infrastructure upgrades. During off-peak hours, ESS stores excess energy that can be used during peak demand periods. This buffer ensures that charging stations have a consistent supply of energy, without overloading the grid or requiring additional power plants.
By acting as a large-scale energy reservoir, ESS alleviates stress on the grid. It provides a reliable energy source for charging stations during high-demand periods, allowing EV owners to charge their vehicles without delays. This reduces the need for extensive grid expansion projects, saving utilities and charging station operators both time and money.
2. Dynamic Load Management
ESS facilitates dynamic load management by adjusting energy storage and discharge based on real-time grid conditions. When the grid is operating at full capacity, ESS can absorb excess electricity and store it for later use. During periods of peak demand, ESS releases stored energy to prevent grid overloads and maintain a stable supply of power for charging stations.
This dynamic approach to energy management helps prevent interruptions in service, ensuring that EV drivers can always access charging stations when needed. It also improves overall grid efficiency by smoothing out demand peaks and preventing grid instability.
Large-scale Energy Storage Solutions
3. Integration with Renewable Energy Sources
ESS plays a critical role in integrating renewable energy sources—such as solar and wind—into the energy mix for EV charging stations. During the day, excess solar energy can be stored in ESS for use at night when solar generation is low. By storing renewable energy in ESS, operators can ensure that charging stations are powered by clean, sustainable energy, even during non-peak hours.
This integration of renewable energy into the charging network helps reduce reliance on fossil fuels and supports sustainability goals. Moreover, it enhances the grid’s overall stability by reducing the pressure on traditional power sources, particularly during peak demand periods.
4. Peak Shaving and Cost Reduction
ESS enables "peak shaving," which involves reducing energy consumption during peak demand periods by using stored energy. By drawing on ESS during high-demand times, charging stations can avoid purchasing expensive electricity from the grid at premium rates. This not only helps stabilize the grid but also reduces operating costs for businesses.
For commercial and industrial charging stations, implementing ESS can lead to significant cost savings. By optimizing energy usage and minimizing peak demand charges, businesses can improve their bottom line while ensuring reliable service for EV drivers.
Integrated Residential ESS Solution
Steps for Implementing ESS in EV Charging Stations
For businesses and utilities looking to integrate ESS into their EV charging infrastructure, several key steps are necessary to ensure success:
- Demand Assessment: Begin by evaluating the power requirements of the charging station and assessing the grid conditions. This helps determine the size and configuration of the ESS system needed to meet demand.
- System Design: Design the ESS to ensure compatibility with existing charging equipment and the grid. The system should also be flexible enough to accommodate renewable energy sources and optimize load management.
- Installation and Commissioning: Install and configure the ESS components, ensuring proper integration with the grid and charging infrastructure. Rigorous testing is essential to ensure the system operates as expected.
- Operation and Maintenance: Once the system is installed, continuous monitoring and maintenance are crucial to ensure optimal performance. Regular updates and inspections will help maintain the efficiency of the ESS and ensure it continues to meet the demands of the charging network.
Conclusion
As the demand for electric vehicle charging stations continues to grow, integrating Energy Storage Systems (ESS) into charging networks is essential for expanding the power grid and ensuring reliable service. ESS helps reduce the need for costly infrastructure upgrades, facilitates dynamic load management, and integrates renewable energy into the grid. By offering a sustainable, efficient solution to grid stress, ESS enhances the resilience and reliability of EV charging stations, making it an attractive investment for businesses in the industrial and commercial sectors.
ESS is the key to a more efficient, sustainable energy future, and for businesses looking to optimize their charging networks, it represents a valuable opportunity to improve performance, reduce costs, and support the transition to cleaner energy.
For tailored ESS solutions that meet the unique demands of your commercial and industrial operations, contact SolarEast today!